Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) combines AI’s pre-trained knowledge with domain-specific knowledge data to provide accurate and context-rich answers. However, building and maintaining RAG workflows can be complex—requiring developers to manage tasks like embedding generation, database updates, and error handling efficiently.
In this blog post, we’ll simplify these concepts with a sample project built using modern Java frameworks and tools, showcasing how JobRunr can streamline your RAG workflows.
Whether you’re a beginner or an advanced developer, this example will demonstrate best practices for automating and scaling RAG-based systems. If you’re curious whether RAG works or not, we provide an example with and without a RAG system at the end of this article.
The Challenges of RAG
RAG’s value is clear. AI models like ChatGPT or LLama have a hard time accurately answering questions about data they haven’t been trained on (which is most likely the case for any proprietary data). RAG has proven to be a simple technique to alleviate this limitation by providing the relevant context to answer a question.
Although the benefits of using RAG are clear, implementing the workflow is not without challenges. Here, we highlight a few:
- Keeping embeddings up-to-date: Knowledge bases are rarely static, they are regularly updated, with addition, update or deletion of documents. Unless providing outdated information to users is acceptable, the embeddings will need to be in sync with the most recent data in the knowledge base.
- Cleaning documents: Some documents contain special syntax used by internal tools, for instance Hugo shortcodes, which makes retrieval and generation more difficult.
- Enriching the data: For better accuracy, document enrichment may be used. This can be done before (adding metadata, or creating a summary) or after (merging a small chunk with surrounding context) retrieval.
- Determining a good chunking strategy: Embeddings are generated from chunks of a document. RAG may fail, if the chunking strategy is not suitable.
- Fine-tuning retrieval process: There are several hyper-parameters to tune such as the similarity threshold between user input and documents in the store or the number of relevant documents to send to the LLM. These parameters have a non-negligible impact on accuracy.
- Evaluating model accuracy: Depending on the enterprise policy, the development team may have to design an evaluation process of the model to ensure that it is safe to release.
Java developers are fortunate to have good frameworks to ease the integration of LLMs into their applications. For example, Spring AI and LangChain4j provide the building blocks for implementing robust RAG, along with other features. However, these tools may not be enough, as issues such as keeping embeddings in sync with knowledge base changes are best handled by job schedulers.
A naive approach would be running the entire RAG workflow at query time as illustrated below: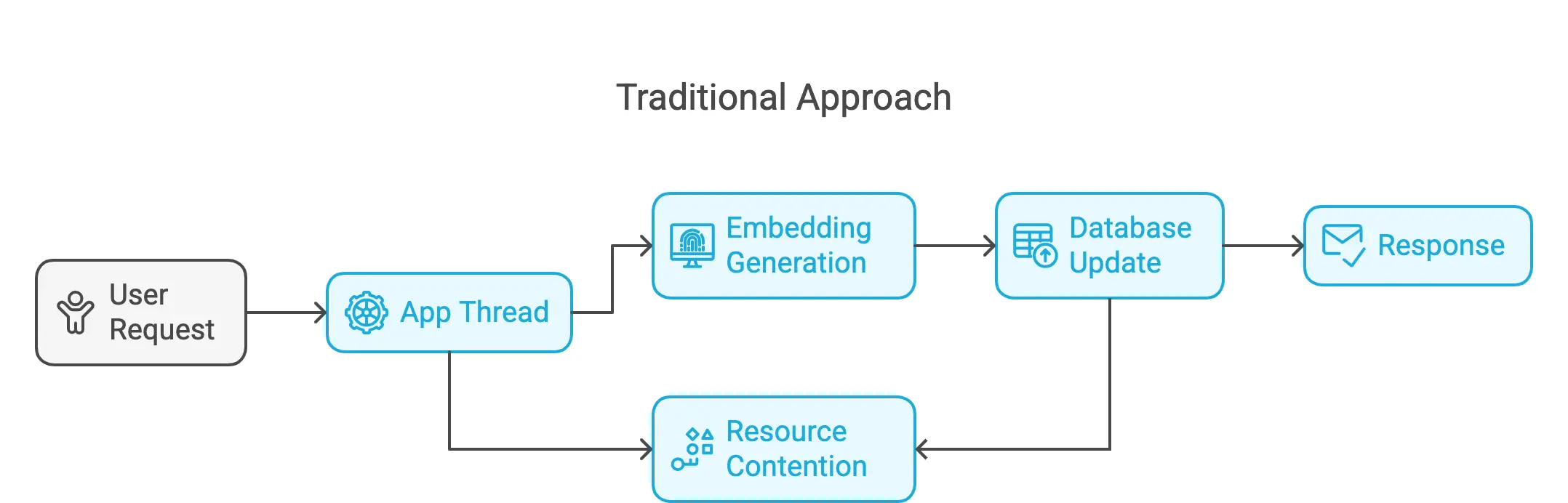
This obviously will not work well beyond very simple applications. One issue is the important wait time for users. Another issue is that the same document may be processed multiple times resulting in wasting resources, unless developers implement a complex resource contention mechanism. Perhaps more importantly, the system may not be able to handle the load as it’s already occupied with other heavy work, a user request at such a time can lead to crashes.
As one improves on this approach, it may start looking more and more like a job scheduler. But implementing a good job scheduler is not a trivial task and may require more time than originally planned as bugs creep in. Without the right tools, you might run into:
- Scalability issues: When big tasks slow down your app.
- Missed jobs: Missed updates or failed jobs can break the system.
- Debugging headaches: Tracking down issues can take longer than expected due to lack of proper monitoring.
These issues take focus away from solving the business problems at hand: ensuring that the LLM accurately answers a user query. JobRunr takes the job scheduling burden away from RAG developers.
How JobRunr helps with RAG workflows
Ronald Dehuysser’s inspiration to connect JobRunr with RAG workflows came from conversations with members of the Spring community. They pointed out that tasks like training large language models and updating embeddings often slow things down when handled synchronously. These challenges naturally aligned with what JobRunr does best: managing long-running tasks in the background.
Here’s how JobRunr fits into the picture:
- Handles tasks without interrupting your app: Embedding creation and database updates run in the background, so your app keeps working smoothly for users.
- Automatic retries for failed jobs: If something goes wrong—like a network glitch—JobRunr automatically retries the job until it’s completed.
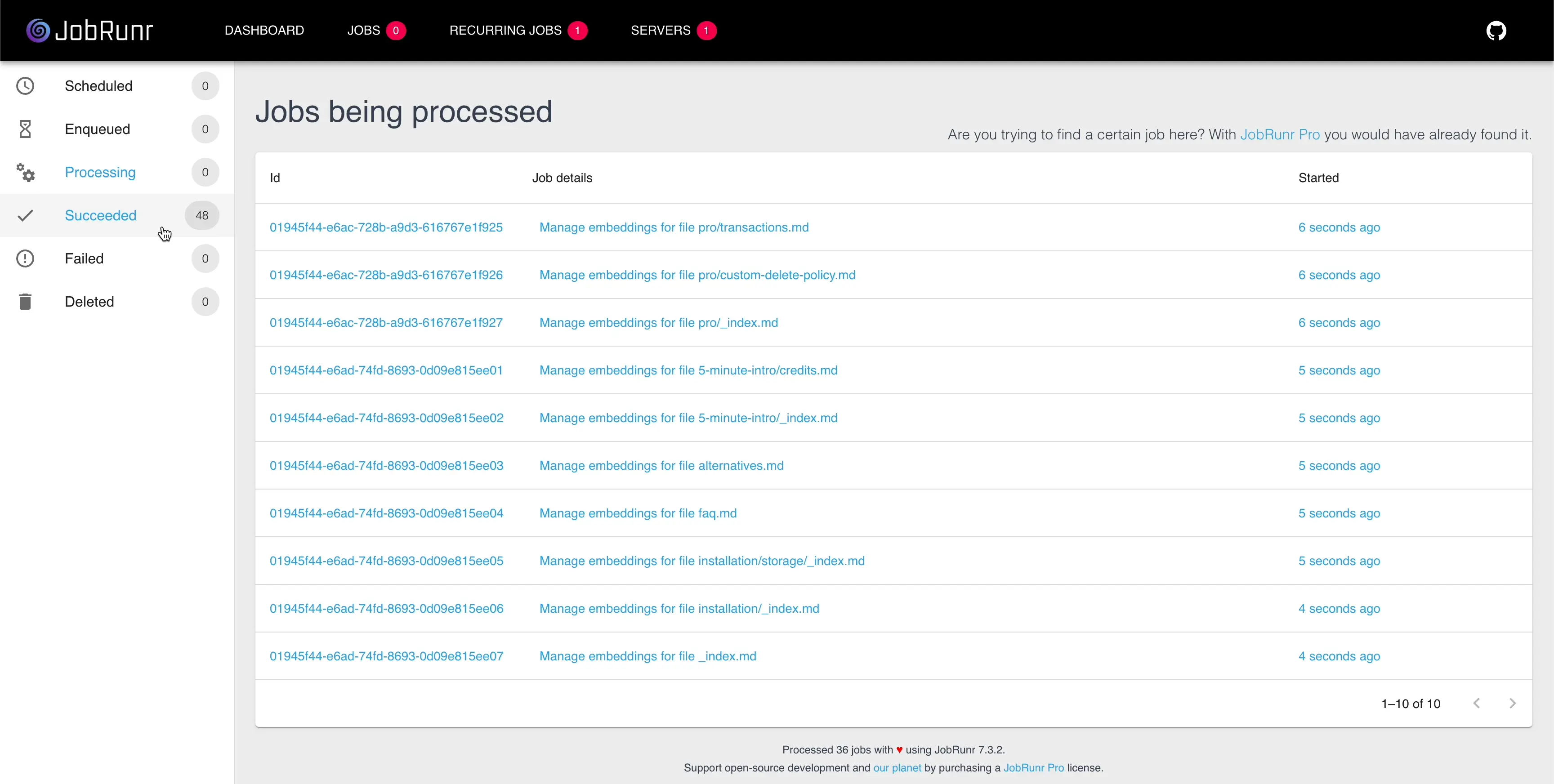
- Easy job tracking: The JobRunr dashboard gives you a clear view of what’s happening, so you can fix issues quickly and re-run jobs if needed.
- Schedules regular updates: Want to update your vector database on a set schedule? JobRunr makes it easy to set up these recurring tasks.
- Handles big workloads: Whether you’re running a handful of tasks or millions, JobRunr scales to meet your needs.
Ronald saw this as a natural fit for RAG systems, where tasks like embedding updates can take time but don’t need to hold everything else up. With JobRunr, you get a setup that works reliably and takes some of the heavy lifting off your plate.
Here’s how JobRunr solves these challenges: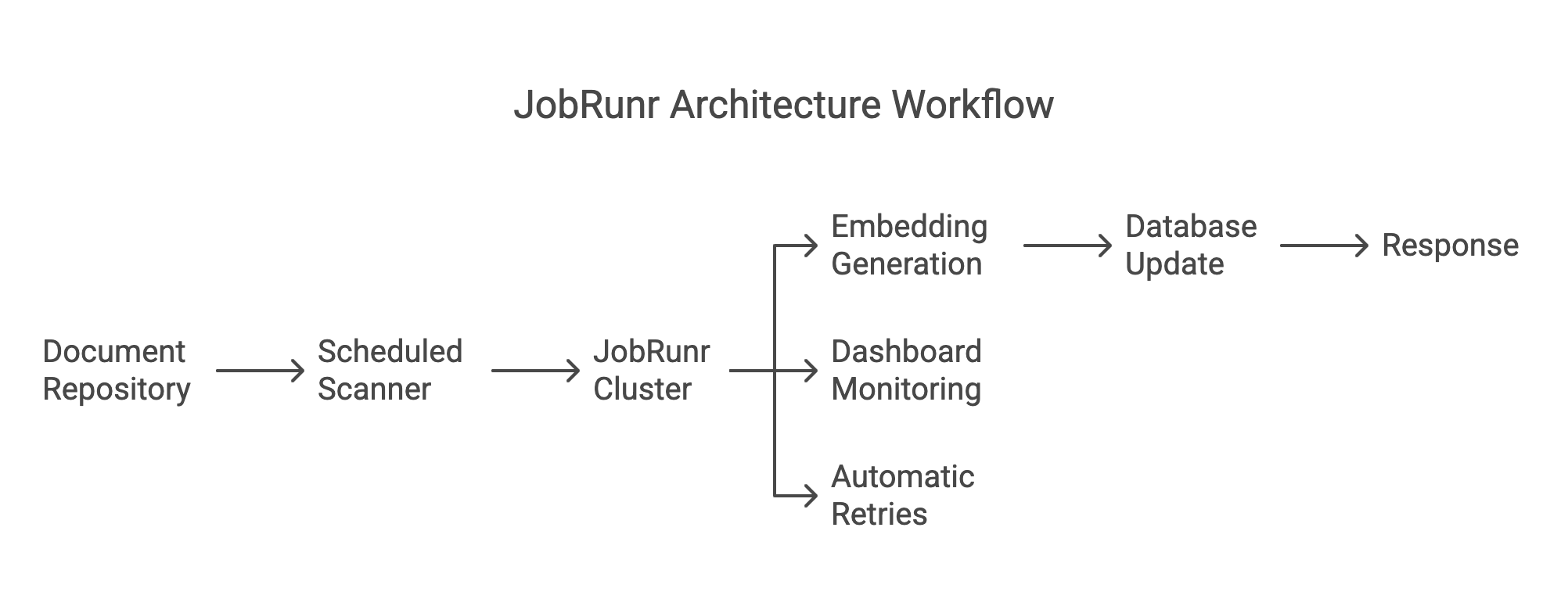
Real-world example: Synchronizing embeddings with JobRunr
In a RAG workflow, keeping embeddings synchronized with document updates is critical.
Let’s walk through an example where JobRunr manages embedding synchronization. To this end, we implement a RAG workflow that manages files in a directory located on the user’s computer, the directory could be a shared one to enable distributed processing.
The project involves two main tasks:
- First, we implement a job that will process a document and update its embeddings. If the document is found to be deleted, the embeddings are removed from the vector store. These tasks will be processed in parallel by the JobRunr workers for efficient embedding synchronization.
- Second, we implement a job to scan our knowledge base, the directory. This task delegates to the document processing task for every modified document it finds in the knowledge base. This task is scheduled recurrently, for example everyday if the directory is expected to change daily. Note: to know when a document is new, updated or deleted, we keep files metadata (relative path, last modified date) in the DB.
Our implementation is modular and can be extended, for example to retrieve documents over HTTP.
For testing purposes, we used JobRunr’s documentation files but the code is designed to work on any directory on your computer.
Step 1: Setup of the example
Our sample project uses the following frameworks and tools:
- JobRunr for job scheduling
- Spring Boot as a java application framework
- Spring AI to integrate LLMs into our sample project
- Ollama to run an LLM locally, we went for a small Llama 3.2
- PostgreSQL with the pgvector extension as database with vector similarity search capabilities
- Flyway for managing database migrations
Follow instructions on Spring AI to initialize a Spring AI project. Spring Initializr will allow you to download a project with of the dependencies we listed above.
If you chose Maven as build tool, you can add JobRunr as follows:<dependency>
<groupId>org.jobrunr</groupId>
<artifactId>jobrunr-spring-boot-3-starter</artifactId>
<version>${jobrunr.version}</version>
</dependency>
Step 2: Update Embeddings with Fault Tolerance
The EmbeddingManager is responsible for processing documents and updating their embeddings. If an embedding exists, it deletes the old data before saving new embeddings. This prevents duplicates we have recently written an article on idempotence highlighting the importance of this logic.
@Job(name = "Manage embeddings for file %0")
@Transactional
public void manage(String relativePath, Status status) {
deleteAllExistingEmbeddings(relativePath);
if (status == UPDATED) {
processDocumentAndSaveEmbeddings(relativePath);
}
}
This snippet demonstrates:
- JobRunr-powered automatic retries: If a job fails due to a temporary issue (e.g., network downtime), JobRunr will automatically reattempt execution. By default the job is retried 10 times with an exponential backoff policy.
- Error handling: Ensures embeddings are updated even if jobs fail intermittently.
This task delegates to Spring AI’s ETL pipeline for embedding generation and storage.
Step 3: Automate Directory Scanning and Job Scheduling
The DirectoryManager class scans a directory for document updates, identifies changes, and schedules jobs to update embeddings—as we have seen this includes deleting them permanently—by delegating to the EmbeddingManager.
@Recurring(id = "embedding-synchronization", cron = "${app.embedding-synchronization.cron}")
@Job(name = "Browse content directory and initiate embedding synchronization")
public void manage(JobContext jobContext) throws IOException {
jobContext.logger().info("Synchronizing embedding files...");
// Get known and current file metadata
List<FileMetadata> knownFiles = fileMetadataRepository.findAll();
List<FileMetadata> currentFiles = getAllFiles();
// Identify updated and deleted files
List<FileMetadata> updatedFiles = getUpdatedFiles(knownFiles, currentFiles);
List<FileMetadata> deletedFiles = getDeletedFiles(knownFiles, currentFiles);
// Schedule jobs for updated files
jobScheduler.enqueue(
Stream.concat(updatedFiles.stream(), deletedFiles.stream()),
file -> embeddingManager.manage(file.getRelativePath(), file.getStatus())
);
// Update metadata in the database
fileMetadataRepository.upsertAll(updatedFiles);
fileMetadataRepository.deleteAll(deletedFiles);
jobContext.logger().info("Synchronization complete. Embedding updates running in background.");
}
This snippet demonstrates:
- JobRunr-powered job scheduling: Embedding updates are automatically queued and processed in a controlled manner.
@Recurringmeans that the task is expected to run recurrently. Notice the value of thecronattribute; it’s a placeholder and developers may configure a cron expression of their choice. - Directory monitoring: Scans the content directory for changes.
- Separation of concerns: Delegates embedding updates to the
EmbeddingManager.
Step 4: Parallelize and Monitor with the JobRunr Dashboard
JobRunr allows you to configure the level of parallelization for processing jobs. This ensures scalability while preventing resource exhaustion.
For Spring Boot, the amount of workers can be configured as simply as:
jobrunr.background-job-server.worker-count=10
If a single machine is not able to handle the workload imposed by your application, you can easily scale to distributed processing by connecting another instance of your application. The only requirement is that all the instances share the same database!
The built-in dashboard provides a clear view of queued, running, and completed jobs. You can manually trigger, requeue, or delete jobs as needed.
This snippet demonstrates:
- Optimized resource utilization: Configurable worker pools ensure jobs run efficiently without overloading the system.
- JobRunr-powered observability: The dashboard allows developers to monitor, retry, and debug jobs with real-time status updates.
Code example download
We’ve prepared a full example project demonstrating:
- Setting up a directory manager.
- Processing documents with content-specific processors (e.g., PDF support via
PdfProcessor). - Using JobRunr to automate and monitor embedding updates.
- A Console application to talk to your RAG model.
👇 Download the project here and get hands-on with JobRunr and RAG workflows.
RAG in action!
Let’s ask our local small LLM, Llama 3.2, a question related to JobRunr. We ask the question with and without RAG.
Prompt: Give me an example of a mutex usage in JobRunr Pro
Answer without RAG (code snippet only):
import io.github.cdimascio.jobrunrJob;
public class MyJob extends Job {
private final Object mutex = new Object();
@Override
public void execute(JobContext context) {
synchronized (mutex) {
// Critical section code here
System.out.println("Accessing shared resource...");
// Perform some work...
System.out.println("Shared resource accessed successfully!");
}
}
}
mutex usage in JobRunrAnswer with RAG:
jobScheduler.create(aJob()
.withMutex("virus-scanner")
.withDetails(() -> System.out.println("This will not run parallel as it is guarded by a mutex"));
@Job(mutex = "virus-scanner")
public void onlyProcessOneJobAtTheSameTime() {
System.out.println("This will not run parallel as it is guarded by a mutex");
}
mutex usage in JobRunrAnyone who knows a little bit of Java would know that the first answer wouldn’t work, unless MyJob is made into a singleton. The code would definitely not behave as expected in JobRunr, where execute is called on new instances of MyJob, unless IoC is in play. Additionally, the job may be executed on different machines. At least the model still gave us Java code—I have seen Go being used at times!
The second answer shows the power of RAG, the answer is directly extracted from the JobRunr documentation. It gives the two flavors for configuring a Job using either the JobBuilder, or the @Job. The answer lacks a bit of an explanation though. But the documentation for these usage examples also lacks explanation…
Why choose JobRunr for your AI workflows?
JobRunr is an ideal tool for developers working on RAG systems due to its:
- Integration with Frameworks: Works out of the box with Spring Boot (👋 Spring AI), Quarkus (👋 LangChain4j, which also integrates with Spring), and other popular Java frameworks.
- Scalability: Handles large-scale tasks effortlessly and can do so in a distributed manner without complex configuration processes.
- Reliability: Fault tolerance ensures embeddings are always up-to-date.
- Ease of Use: An intuitive API to reduce the learning curve and a dashboard for monitoring and increasing productivity.
Whether you’re automating customer support, processing financial data, or managing medical research workflows, JobRunr can help you simplify these operations.
Start streamlining your RAG workflows today with JobRunr. Download the free version or explore the advanced features of JobRunr Pro.
FAQ
How does JobRunr enhance RAG workflows?
JobRunr automates job scheduling and error handling, making RAG workflows simpler, reliable, and easier to scale. It simplifies embedding synchronization by allowing developers to create functions or methods and control the level of parallelization. Additionally, JobRunr retries failed jobs automatically if, for instance, a resource like a URL is temporarily unavailable.
Can JobRunr handle vector database integration?
Yes, JobRunr supports many databases, e.g., PostgreSQL with a pgvector extension, ensuring efficient storage and retrieval for RAG systems. It can be easily extended to support any DB of your choice.
What are the benefits of using JobRunr in Java AI projects?
JobRunr offers parallel processing, fault tolerance, and real-time monitoring, making it ideal for AI workflows built with Java.
How do I set up JobRunr with Spring Boot?
JobRunr integrates out of the box with Spring Boot. Simply include the JobRunr Spring Boot Starter dependency and configure it in your application to get started.
Why is embedding synchronization important in RAG systems?
Because knowledge bases are regularly updated, embedding synchronization ensures that AI models always have access to the most up-to-date information, improving the accuracy and relevance of their responses.
Can JobRunr handle large-scale RAG workflows?
Yes, JobRunr is able to handle distributed processing, making it capable of handling workflows with over millions of documents, where a single machine may struggle.
Where can I download the JobRunr example project?
You can download the full example project, which includes directory management, embedding updates, and JobRunr configuration, here.
What is a vector store, and why is it used in RAG?
A vector store, such as pgvector, stores embeddings in a format optimized for similarity searches, enabling efficient retrieval in RAG workflows.
How do I monitor jobs in JobRunr?
JobRunr provides a built-in dashboard that offers real-time visibility into job statuses, allowing you to monitor, debug, and manage tasks effectively to proactively address issues if any.