What is a job scheduler in Java?
In Java, a scheduler is a tool that allows the execution of tasks or jobs at a given time, interval, or condition. A scheduler allows to reliably automate tasks such as mass emailing, document/image processing (e.g, medical image analysis, or RAG chatbots), order fulfilment, notification management, reporting, and more. It has the potential to simplify workflows and increase productivity through retry mechanisms that reduce errors and manual intervention.
Job schedulers are obviously well suited for batch processing, but they are really suited for any task that can be delayed (e.g., a registration confirmation email). Their use allows greater control over computing resources, preventing system overloads and keeping costs under control.
Given the benefits and capabilities, job schedulers are a valuable addition to a wide range of industries, including healthcare, finance, and e-commerce. They are especially important for applications where workload automation is mission critical.
Using a good job scheduler greatly reduces the burden on teams, allowing them to focus on innovating instead of maintaining.
What makes a good scheduler?
A good job scheduler is a tool that allows developers to automate and manage tasks in a transparent and straightforward way, while ensuring reliability and scalability. Here are the key features, we believe, a good scheduler should have:
- Essential scheduling features: a scheduler should be able to handle one-time scheduling (for fire-and-forget or delayed tasks) and recurring scheduling (e.g., for cron jobs). Under normal circumstances, the scheduler should also ensure that once registered, a task is executed, once and only once—so no parallel execution of the same task.
- Developer-friendly: tools should not get in the way of solving actual business problems and hinder productivity. Therefore a job scheduler should be easy-to-use, with a simple straightforward API, and easy to integrate into existing applications. Additionally, the scheduler should possess an extensible architecture.
- Fault tolerance: schedulers should have mechanisms to handle errors, and automatically retry jobs should be built-into the system to ensure that tasks are successfully completed even under unpredictable conditions (e.g., network failure, unexpected system shutdown, etc.). Fault tolerance indirectly increases productivity, as developers will no longer need to monitor the system closely and manually restart failed processes. This important feature is often missing or incomplete in simpler schedulers.
- Distributed processing: processing of tasks across multiple servers is a must for systems that should never go down (thus requiring high availability) or where the expected load cannot be handled by a single machine.
- Real-time monitoring: asynchronous job processing systems are opaque, often we do not know when a task starts or finishes. Without realtime monitoring capabilities to provide visibility into task execution, a failure may go unnoticed for days. The scheduler should make it easy to identify and proactively resolve issues.
- Reliability: a job scheduler should be well tested and actively maintained to evolve with user needs and fix critical bugs. Furthermore, a job scheduling tool, should keep its number of third-party dependencies to a minimum, for better security insurance.
To summarise, a good scheduler is one that is easy-to-use, reliable, and designed to meet the demands of modern applications. With these features, it enables teams to easily automate workflows, while ensuring stability and scalability.
JobRunr ticks all these boxes, making it the ideal choice for teams looking to improve their workload automation and increase productivity.
Of course, a scheduler can have more features than those listed, such as priority queues, multi-tenancy, rate limiting, etc., which makes it even better, as long as they do not make it more complex.
Choosing the best Java job scheduler
There are many job scheduling frameworks in Java: the standard built-in java.util.TimerTask and java.util.concurrent.ScheduledExecutorService or third-party job schedulers such as JobRunr, DB-Scheduler and Quartz.
Choosing the best scheduler may come down to personal preferences. However, JobRunr stands out from its competition by offering a number of advantages over the traditional frameworks:
- a really easy fluent API that allows you to enqueue or schedule java tasks with just one line of code or by means of the
@Recurringannotation - an embedded job scheduler dashboard showing you the status of each job
- distributed job execution over different JVM instances
- integration with various frameworks including Spring Boot, Micronaut and Quarkus.
Loved and used by developers from all horizons, JobRunr combines modern, lightweight, and easy-to-use features with enterprise-grade capabilities, providing reliability, security, and support for large-scale production deployments. In comparison, frameworks like Quartz feel really heavy and complex.
What types of job scheduling exist?
When it comes to job scheduling in Java, there are three main types of scheduling to consider: direct execution, scheduled execution in the future, and recurring execution using a cron expression.
Direct execution (aka fire-and-forget): This type of scheduling is used when you want a job to be executed
immediatelyas soon as possible (because execution is asynchronous and other tasks may already be in the queue or processing). This makes it ideal for one-off tasks or to distribute load over multiple servers. JobRunr allows to create a one-time job by means of theenqueuefunction on theBackgroundJobclass or theJobSchedulerclass.BackgroundJob.enqueue(() -> System.out.println("This will run asap and perhaps even on another server"));Scheduled (aka delayed) execution in the future: This type of job scheduling allows you to schedule a task for execution at a specific time in the future. This is useful for tasks that need to be executed at a specific time, such as sending out reminders or triggering reports. To do so, you can use the
schedulemethod in JobRunr:BackgroundJob.schedule(Instant.now().plus(5, DAYS), () -> System.out.println("This will run 5 days from now!"));Recurring execution using a cron expression: This type of scheduling allows a job to be executed repeatedly at a set intervals, such as daily, weekly, or monthly.
BackgroundJob.scheduleRecurrently("*/5 * * * *", () -> System.out.println("This will be printed every 5 minutes!"));
Guide to implementing job scheduling in Java using JobRunr
Getting started with job scheduling in Java is simple and fast—you can be up and running in just 5 minutes! In this example, we’ll use the JobRunr Spring Boot Starter to quickly add background job scheduling to your Spring Boot application.
1. Add the JobRunr dependency to your project
Using your build tool of choice, add the JobRunr scheduler dependency to your Spring Boot project. This can be done by adding the jobrunr-spring-boot-3-starter artifact. In this guide, we’ll be using Maven in this example, so we need to have the following declared in our pom.xml:
<dependency>
<groupId>org.jobrunr</groupId>
<artifactId>jobrunr-spring-boot-3-starter</artifactId>
<version>7.4.1</version>
</dependency>
2. Make sure you have a StorageProvider
JobRunr will need to save your jobs in a SQL or NoSQL database by means of a StorageProvider—making job scheduling independent of application life-cycle. Thanks to the jobrunr-spring-boot-3-starter, JobRunr will automatically try to use your existing DataSource. In this example, we will use the H2 Database. To do so, also add the H2 dependency to your pom.xml.
<dependency>
<groupId>com.h2database</groupId>
<artifactId>h2</artifactId>
</dependency>
H2 is just one of many databases supported by JobRunr, find out more here.
3. Configure JobRunr using Spring’s application.properties.
To configure JobRunr, you can leverage the application.properties file from Spring Boot. In this example, we will enable all off JobRunr’s features including the actual job processing and the scheduler’s Web UI (for monitoring purposes).
org.jobrunr.background-job-server.enabled=true
org.jobrunr.dashboard.enabled=true
4. Start creating jobs using JobRunr’s java job scheduler API
Create a fire-and-forget job:
Now that we have setup our dependencies, we can easily create fire-and-forget jobs using the enqueue method:
@Inject
private JobScheduler jobScheduler;
jobScheduler.enqueue(() -> myService.doWork());
JobScheduler beanThis line makes sure that the lambda—including type, method, and arguments—is serialized as JSON to persistent storage (an RDBMS like Oracle, Postgres, MySql, and MariaDB or a NoSQL database).
A dedicated worker pool of threads running in all the different BackgroundJobServers will then execute these queued background jobs as soon as possible, in a first-in-first-out manner. JobRunr guarantees the execution of your job by a single worker by means of optimistic locking.
Schedule a job in the future:
We can also schedule jobs in the future using the schedule method:
@Inject
private JobScheduler jobScheduler;
jobScheduler.schedule(now().plus(8, HOURS), () -> myService.doWork());
Schedule a recurrent job using a cron expression:
If we want to have recurrent jobs, we need to use the scheduleRecurrently method:
@Inject
private JobScheduler jobScheduler;
jobScheduler.scheduleRecurrently(Cron.daily(), () -> myService.doWork());
5. Visit the Web UI and see how your jobs are doing!
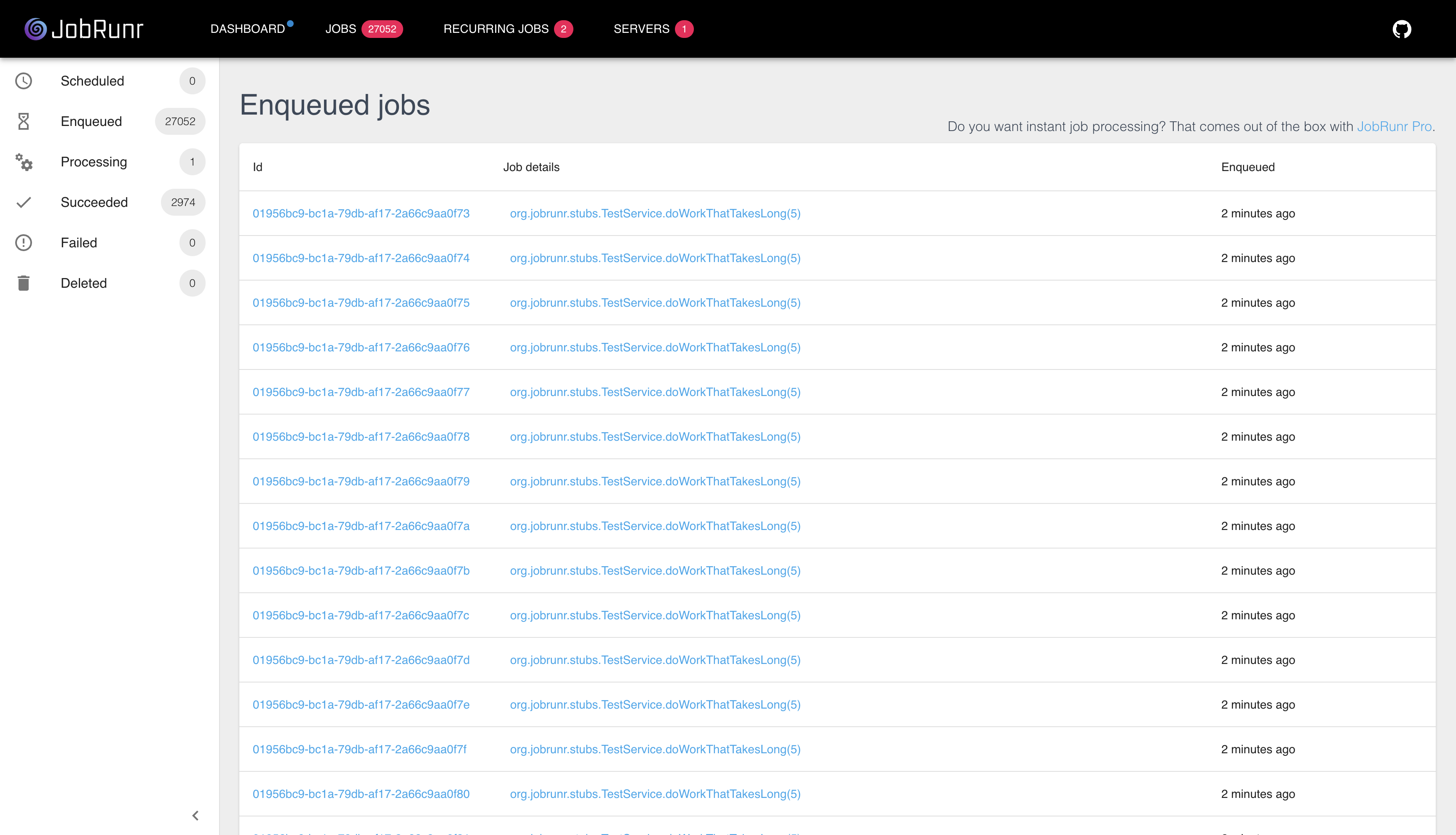
The dashboard provides an overview of all enqueued jobs, and other states, helping you track the status of each job and ensure reliable execution.
Conclusion
JobRunr is probably the best choice for a scheduler in any Java project. With its modern features and simple API, you can quickly and easily create one-off jobs, schedule jobs to run at a specific time or after a specific interval.
JobRunr’s enterprise-grade capabilities ensure reliability, security, and support for large-scale production deployments, making it the ideal choice for any Java scheduling needs. And, it also comes with great support if you take a JobRunr Pro license.
FAQ
1. What is job scheduling in Java, and why is it essential?
Job scheduling in Java automates task execution at specific times or intervals, reducing the need for manual intervention and improving efficiency. Scheduling ensures that background jobs run in an organized order, prevents system overload, and manages complex workflows—all crucial for high-performing applications.
2. How does JobRunr’s Java job scheduler handle task automation?
JobRunr’s Java job scheduler integrates easily with popular frameworks like Spring Boot, enabling you to enqueue tasks, schedule jobs for future execution, or set up recurring tasks using cron expressions. Its job scheduler dashboard provides real-time monitoring, making it simple to manage and track background job performance.
JobRunr’s workers, if enabled, will regularly check the database for newly submitted jobs via the JobScheduler API. If a job is found, the worker that retrieved it, will start executing the task.
3. What types of job scheduling does JobRunr support?
JobRunr supports three main types of job scheduling:
- Direct execution (aka fire-and-forget) for immediate tasks.
- Scheduled execution in the future (aka delayed) for tasks set to run at a later time.
- Recurring execution with cron expressions or fixed intervals for periodic or repeating jobs, such as daily or weekly tasks.
4. Can JobRunr schedule tasks across multiple servers with distributed job scheduling?
Yes, JobRunr’s distributed job scheduling feature allows tasks to execute across multiple JVM instances, improving scalability and enabling efficient task management in multi-server environments.
5. How does JobRunr’s job scheduler dashboard help with task monitoring?
The Web UI in JobRunr provides a comprehensive view of each job’s status, including completion history and any errors encountered. This makes it easier for teams to monitor job performance, troubleshoot issues, and optimize resource usage.
6. What is a cron expression, and how is it used for recurring jobs?
A cron expression is a syntax that defines intervals for recurring job scheduling, such as daily, weekly, or monthly tasks. JobRunr enables you to use cron expressions for repetitive tasks, making it easy to automate ongoing processes like generating reports or sending reminders.






